 |
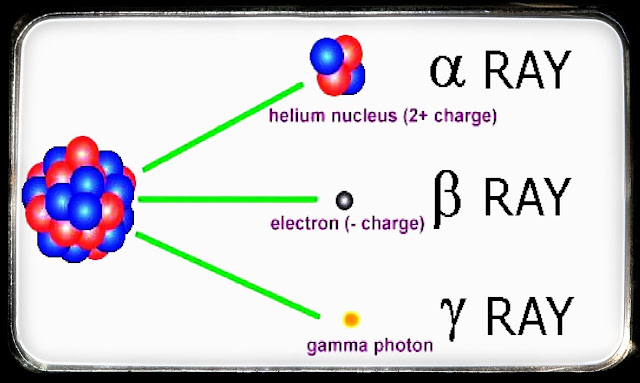
Early discovery of the types of alpha, beta and gamma raysIn 1903, Ernest Rutherford suggested that the radiation emitted by radioactive substances can be divided into two types based on their charge. Radiation that is positively charged is called alpha rays, and that which is negatively charged is called beta rays. Furthermore, Paul U. Viillard discovered the third type of ray that has no charge and was named gamma rays. |
a. Alpha rays (α)
Alpha rays are positively charged particle radiation. The alpha-ray particles are the same as the helium nucleus -4, with a charge of + 2e and a mass of 4 amu.
Alpha particles are the heaviest particles produced by radioactive substances. Alpha rays are emitted from the nucleus at about 1/10 the speed of light.
Because it has a large mass, alpha light penetrates the weakest among radioactive rays. In the air it can only penetrate a few cm and cannot penetrate the skin.
Alpha rays can be stopped by a plain sheet of paper. Alpha rays immediately lose their energy when they collide with the media molecules in their path.
The collision resulted in ionization of the media through which it passed. Finally the alpha particles will capture 2 electrons and turn into H42 atoms.
b. Beta rays (β)
Beta rays are negatively charged particle radiation. Beta rays are an electron beam that comes from the atomic nucleus.
Beta particles that have a charge of -1e and have a mass of 1/836 amu. Because they are so small, beta particles are considered massless and are represented by the notation 0-1e.
The energy of beta rays varies widely, has a greater penetrating power than alpha rays but has weaker ionizing power. The most energetic beta rays can travel up to 300 cm in dry air and can penetrate the skin.
c. Gamma rays (γ)
Gamma rays are high-energy, chargeless and massless electromagnetic radiation. Ray γ is represented by the notation 00γ.
Gamma rays have penetrating power. Apart from alpha, beta, gamma rays, there are also artificial radioactive substances that emit X-rays and Positron rays. X rays are electromagnetic beam radiation.
