Sensor with temperature change
This sensor works because of changes in temperature around the sensor, the detection results in the form of non-electrical signals are converted into electrical signals, usually in the form of electrical voltage. And generally every change in 10°C produces a voltage of 1mV dc.
Temperature sensors have several models and types of temperature sensor examples on the market, including PTC, NTC, PT100, LM35, thermocouple and others. The following are characteristics of several types of temperature sensors.
 |
| Figure Characteristics of several types of temperature sensors |
In the picture above, the IC sensor and thermocouple have the best linearity, but because in this task the temperature measured is more than 100°C, the thermocouple is the most suitable because it is able to reach a temperature of 1200°C. While the linear sensor IC is capable of up to 135°C.
PTC and NTC Thermistor or thermal resistance is a semiconductor component that has the character of a resistance with a high coefficient of temperature resistance, which is usually negative. There are 2 types of thermistors that we often encounter in electronic devices, namely NTC (Negative Thermal Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Thermal Coefficient).
Generally, the thermistor resistance at room temperature can be reduced by 6% for every 1°C increase in temperature. This high sensitivity to temperature changes makes the thermistor very suitable for precise temperature measurement, control and compensation.
 |
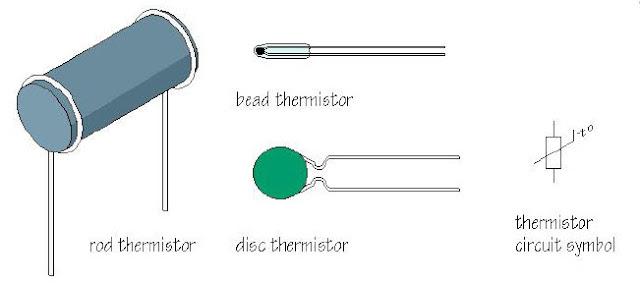
| PTC and NTC thermistor images and symbols |
Thermistors are made from a mixture of precipitated metal oxides such as: manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), iron (Fe) and uranium (U). The resistance range is from 0.5 W to 75 W and is available in various shapes and sizes. The smallest size is in the form of beads (beads) with a diameter of 0.15 mm to 1.25 mm, the shape of a disk (disk) or ring (washer) with a size of 2.5 mm to 25 mm. The rings can be stacked and placed in series or parallel to increase power dissipation.
The temperature coefficient is defined at a certain temperature, for example 25°C as follows: