What are the functions of lysosomes in animal cells?
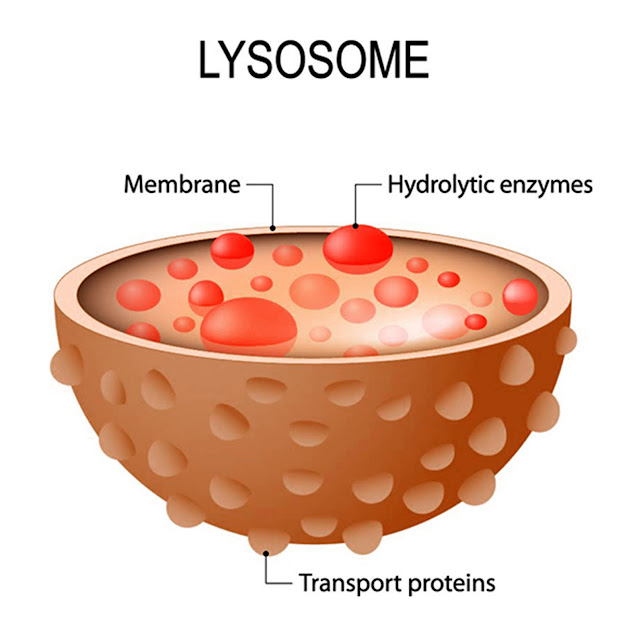
The function of lysosomes in animal cells has an important role in animal digestion. Scientists say that lysosomes have a pocket-like shape. This bag is bound to a membrane in which there are many hydrolytic enzymes. There are approximately 40 to 50 types of enzymes in it.
The functions of lysosomes are endocytosis, phagocytosis, and autophagy. Lysosomes are cell particles that have a size between the microsome and mitochondria and have a shape like a vacuole which contains hydraulic enzymes and is useful in controlling intracellular digestion.
Do lysosomes play a role in autotomy?
The characteristics and functions of lysosomes include being an organelle that performs autophagy, destroys damaged cell organelles, is formed by the Golgi body, the enzymes contained in it are formed by ribosomes, also play a role in autotomy and the loss of tails in frogs as adults.
In the cell are there lysosomes explain?
Lysosomes are bag-shaped organelles that contain digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are useful for digesting waste, food, or foreign substances. When the lysosome breaks, the enzymes in it will digest or destroy the cell organelles and consequently the cell will die. Lysosomes exist only in animal cells and not in plant cells.
Are lysosomes the same as vacuoles in plants?
Lysosomes are cell organelles in the form of membrane-bound pouches containing hydrolytic enzymes that are useful for controlling intracellular digestion under various conditions. In plants this organelle is better known as a vacuole, which in addition to digesting, has the function of storing organic compounds produced by plants.
What are the functions of lysosomes in cells if they are deficient in enzymes?
The lysosome itself is an organ in the body's cells that functions to digest compounds, such as carbohydrates and proteins. If the enzymes needed to carry out its functions are deficient, the compounds in the body will accumulate and become toxic.
What are the functions of the hydrolytic enzymes present in lysosomes?
Hydrolytic enzymes are often referred to as digestive enzymes because the main function of this enzyme is to digest or break down (from the word lysis). Hydrolytic enzymes are enzymes found in small, webbed organelles called lysosomes. Hydrolytic enzymes are able to control intracellular digestion under various conditions.
What happens if the lysosome malfunctions?
The lysosome will die and rot, usually it will be eaten by other lysosomes, otherwise it will come out of the body and will become pus.
What happens if the lysosome in the cell breaks?
With the breakdown of the lysosome, all forms of enzymes will be shed. These enzymes will degrade all the molecules that become their substrates. Usually, the substrate of the enzymes of the lysosome is a macromolecule causing the macromolecule to degrade.
Why are lysosomes only found in animal cells?
Lysosomes are only present in animal cells. Plant cells do not have lysosomes because they already have vacuoles that have the same function as lysosomes. The function of vacuoles is to digest and store organic compounds produced by plants.
What is meant by primary lysosomes?
There are 2 types of lysosomes according to their function, namely primary lysosomes and secondary lysosomes. Primary lysosomes are lysosomes whose job is to produce enzymes that are not yet active. The primary lysosome functions as a food vacuole.