Pest control on ginger plants is a control measure taken to prevent losses in ginger cultivation caused by pests by combining one or more control techniques combined in one unit. The aim is to reduce the risk of loss of cultivation and improve quality and preserve the environment.
Mimegralla coeruleifrons Macquart pests
- Order: Diptera
- Family: Micropezidae
Rhizome Fly Host Plants (Mimegralla coeruleifrons Macquart): Ginger, turmeric, Kaempferia galanga, ginger, Curcuma aeruginosa.
Symptoms of Rhizome Fly (Mimegralla coeruleifrons Macquart) on ginger
- Symptoms of rhizome fly attack are difficult to distinguish from attacks of wilt disease;
- After 8-10 days the ginger plant looks yellowish and dries up, starting from the lower ginger leaves followed by all the leaves;
- Severe attacks cause ginger plants to wilt and dry up, while the rhizome is porous;
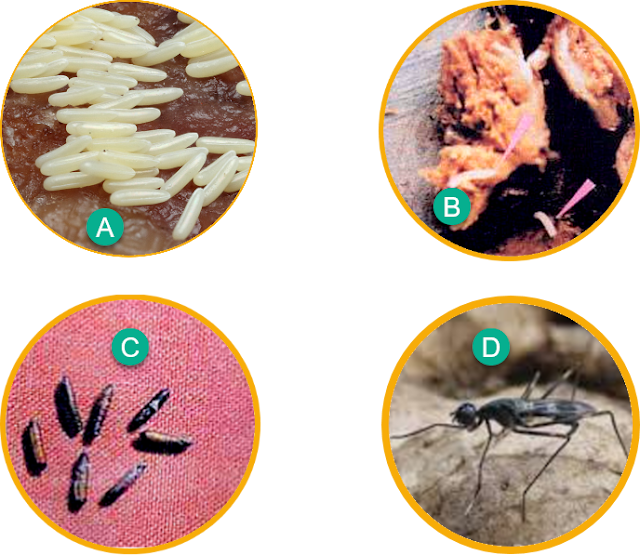 |
Image of Mimegralla coeruleifrons rhizome fly pest a. Egg b. Larva c. Pupa d. Adult fly insects |
Control
a) Technical culture
- Not planting intercropping ginger with turmeric or other plants of the Zingiberaceae family which are host plants for this pest;
- Sorting rhizomes before planting;
- Strive for healthy plant growth, free from wilt disease or other diseases;
- The use of patchouli as a barrier and intercropping it with ginger can reduce the population of rhizome flies;
- Sanitation by cleaning the plant from plant debris and destroying it.
b) Biological
Utilizing natural enemies, namely larvae-pupa parasitoid Trichopria sp. (Diapriidae, Hymenoptera), and the fungus Beauveria bassiana which infects larvae.
c) Chemical
Use of insecticides to control adult flies. Insecticide that is registered and permitted by the Ministry of Agriculture for ginger pests.
