 |
| Although the energy accumulated by radioactive rays in living things is relatively small, it can have serious effects. This is because radioactive rays can cause ionization, breaking important chemical bonds or forming reactive free radicals. |
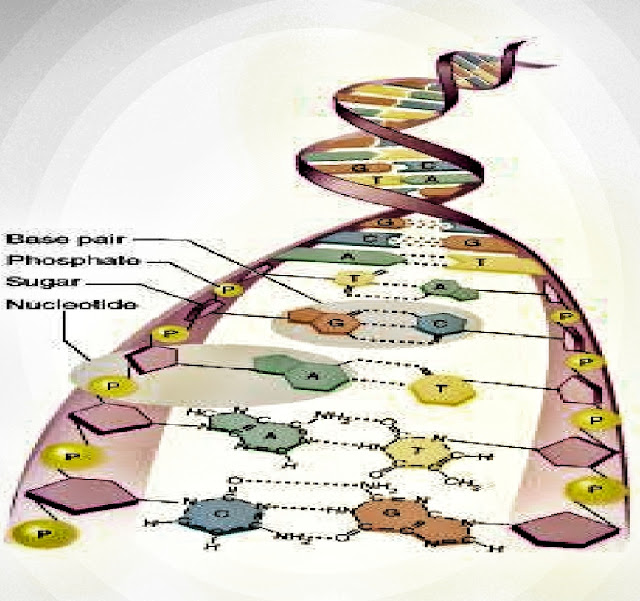
Chemical bonds are important, for example, bonds to DNA structures in chromosomes. Changes that occur in the DNA structure will be passed on to the next cell which can lead to genetic disorders, cancer, etc.
The effect of radiation on humans or living things also depends on the time of exposure. A dose received at one time is more dangerous than if the same dose is received for a longer time.
Naturally we get radiation from the environment, for example cosmic ray radiation or radiation from natural radioactivity. In addition, from various activities such as diagnosis or therapy with X rays or radioisotopes.
People living near nuclear installations also receive more radiation, but still within safe limits.
